Introduction
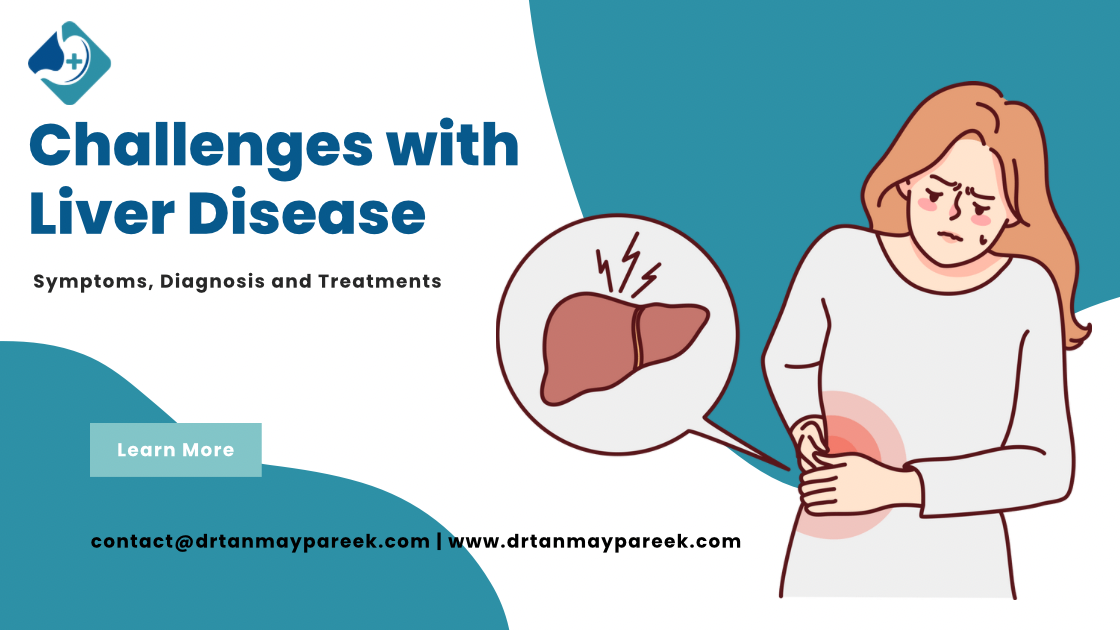
Liver disease is a growing concern in India, affecting a significant portion of the population. The
liver plays a vital role in digestion, detoxification, and metabolism, making liver health crucial for
overall well-being. Understanding the common types of liver diseases and their management
can help individuals live healthier lives.
Common Liver Diseases
Several liver diseases are prevalent, including:
- Hepatitis: This viral infection causes inflammation of the liver and can be acute or chronic.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Often linked to obesity and poor dietary habits, this condition involves the
accumulation of fat in the liver. - Cirrhosis: This is the scarring of the liver due to long-term damage, which can lead to liver
failure. - Liver Cancer: A serious condition often arising from chronic liver diseases, particularly
cirrhosis.
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Many liver diseases develop without noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, some
common symptoms include:
- Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and eyes due to the buildup of bilirubin.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness can be a sign of liver dysfunction.
- Abdominal Swelling: Fluid buildup in the abdomen, known as ascites, may occur.
- Changes in Appetite: Unexplained weight loss or a decrease in appetite can signal liver issues.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors for liver disease is essential for prevention:
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can lead to liver damage and disease.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases the risk of fatty liver disease and other liver problems.
- Viral Infections: Hepatitis viruses can cause chronic liver disease.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol can contribute to liver
disease.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
If liver disease is suspected, various tests can help diagnose and monitor the condition:
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) assess liver health and function.
- Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs can visualize liver abnormalities.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the extent of liver
damage.
Treatment Options
The treatment for liver disease varies depending on the specific condition:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight loss, a balanced diet, and regular exercise can significantly
improve liver health. - Medications: Antiviral medications for hepatitis or treatments for fatty liver disease may be
prescribed. - Surgery: In severe cases, such as liver cancer, surgical interventions or liver transplantation
may be necessary.
Coping with Liver Disease
Living with liver disease can be challenging, but support is available:
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Mental Health Considerations: Counseling or therapy may help individuals cope with the
psychological impacts of liver disease. - Regular Follow-ups: Consistent monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider
are vital for managing liver disease effectively.
Conclusion
Prioritizing liver health is essential for overall well-being. Understanding liver diseases and their
implications can empower individuals to take charge of their health. If you suspect liver issues or
have been diagnosed with a liver condition, consult Dr. Tanmay Pareek for personalized care
and treatment plans tailored to your needs.